Finance-Grade Sustainability Data
Learn about finance-grade sustainability data and how it unlocks business opportunities
The Opportunity for Sustainability Teams
In an era of voluntary reporting, sustainability teams have been figuring out what to report and how to smooth out the glitches their semi-automated data preparation systems. But 2025 is the start of a new era. Regulatory reporting requirements are sticking and also expanding each year. Reported data speeds its way to investors, who scrutinize it closely. And top leadership is requiring that sustainability teams prepare a business case for every proposed savings project.
All of these trends move sustainability closer to an everyday business function. And when sustainability teams can deliver high-quality data that serves reporting, investor and CFO needs, sustainability teams can literally change their role, delivering company-wide profit and value creation.
Finance-grade sustainability data is key to unlocking this change. Not only does it meet stakeholder needs, it has the accuracy, reliability, speed, and compliance of financial data. If years ago the saying was “you can’t manage what you don’t measure,” today the saying is, “your impact is driven by your data quality.”
What is Finance-Grade Sustainability Data?
Very simply put, finance-grade sustainability data is used and trusted by two key constituencies. First, it is used and trusted by sustainability, finance and capital budgeting to build a business case for change, such as forecast of cash savings from an energy reduction project. Second, it is used to make financial decisions by banks, investors and other lenders. When sustainability data can survive this double round of scrutiny, it is finance-grade.
Without this high-quality data, sustainability teams are stuck. Their plans for reducing emissions use capital, but no one is confident they return savings. Investors and lender are not willing to believe the coarse business case either.
In sum, finance-grade sustainability data is trusted by others as they make business decisions. The phrase “accurate, reliable and decision-useful” summarizes the purpose of an audit in finance or sustainability, e.g. “can an external party trust this data when spending millions of dollars?” Finance-grade data meets that need.
How to Get Finance-Grade Sustainability Data
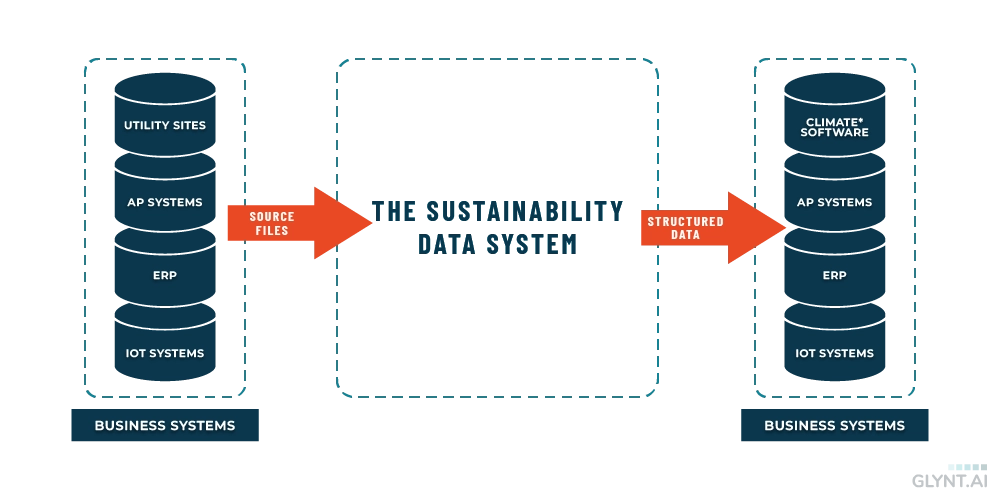
Sustainability reporting has been a multi-year journey for most companies, and this is true of their data preparation systems as well. As the graphic below shows, the data system sits between the scattered source files and the reported data. Finance-grade data is produced by a high-quality data system.
As part of the “sustainability journey,” companies go through several stages of sustainability data preparation, from simple reporting to more complex systems. GLYNT.AI has found that these systems can be categorized into four general types, each with its own level of automation and data quality.
The four tiles below show the types of data systems we’ve encountered. Less automated systems are less accurate, and systems that lack consistent data sets year over year are less reliable.
THE SUSTAINABILITY DATA SYSTEM
FOUR TYPES OF SUSTAINABILITY DATA SYSTEMS
Reporting
- Used to submit annual reports
- Site-level, 10 fields
- No automation
- Low accuracy
- Low reliability
Tracking
- Used to report and track reductions annually
- Site-level, 10 fields
- No automation
- Add data QA
- Medium accuracy
- Low reliability
Audit-Ready
- Audited data to report and track reductions
- Site-level, 10+ fields
- Semi-automated
- Data QA, audit-ready documentation, verification checks
- High accuracy
- Medium reliability
Integrated Reporting
- Accurate, audit-ready, financially compliant data and reporting
- Extensible from sites to meters, sub-meters and PCF
- Fully automated
- High accuracy
- High reliability
Data Reliability by Type of Data System
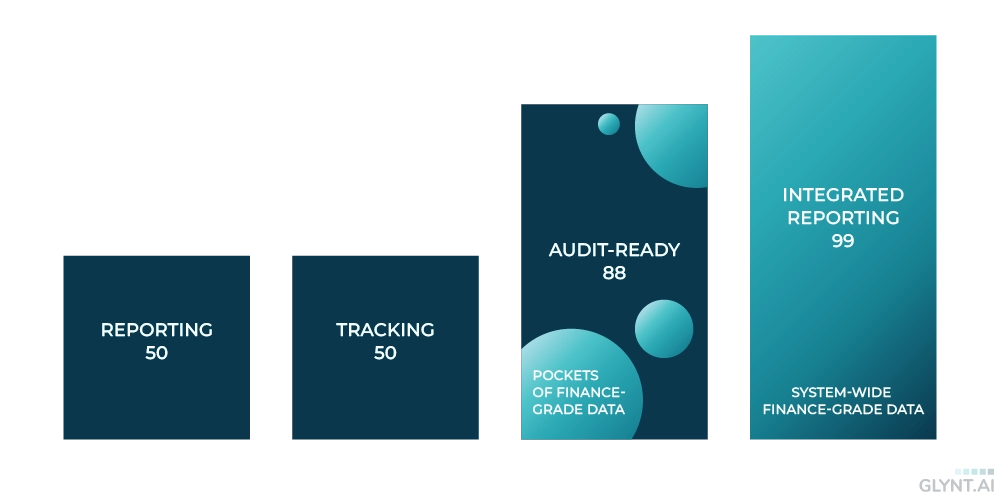
The second finding is that Integrated Reporting – in which each transaction in sustainability data is tied to a transaction in the financial system – leads to much more consistent and explainable data sets. This increases reliability significantly. It is not enough to be audit-ready, one must have consistency in data sets reported too.
To sum it up, Integrated Reporting produces finance-grade sustainability data. Audit-ready data may have pockets of reliability and with extra work one can build a reduction plan for selected sites or assets.
Better data need not cost more money. Automated sustainability data services like GLYNT.AI provide Integrated Reporting at a lower cost than even in-house reporting. Thanks to automation and AI, there is no need to make a tradeoff between cost and data quality.
Read the Guide to GLYNT.AI’s Sustainability Data TCO Calculator
Finance-Grade Data Transforms the Role of Sustainability
Automation and data quality go hand in hand and enables finance-grade sustainability data. Automation enables many more accuracy and validation tests and ensures that they are done across the entire dataset, not just on the pockets of data where a human reviewer happened to work. Automation is needed to tie the sustainability data set to an external record, such as an accounting transaction, a procurement records and so on. As the graph below shows, a higher level of automation is needed to achieve higher levels of data quality. In sum, finance-grade data can meet its two key use cases – use by the internal finance team and use by investors and lenders – because it is automated.
Finance-Grade Sustainability Data Unlocks Opportunity
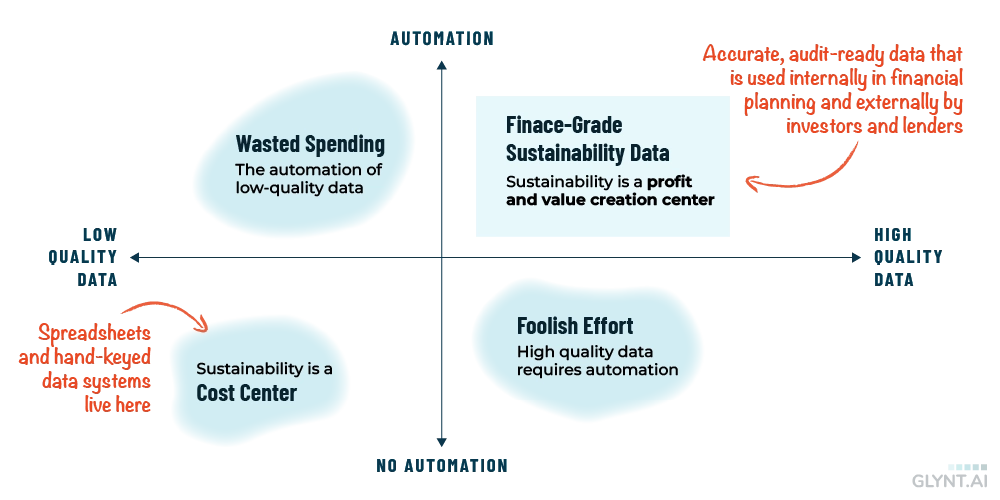
And progress is powered by the business case for each savings project. A business unit that gets their projects approved by finance and capital budgeting teams, and has the option to secure outside financing, is a center of profit and value creation. Finance-grade sustainability data opens that door.
Ready to Talk with GLYNT about Financial-Grade Sustainability Data?
Please contact us, we’d love to hear your data story!
More Like This
For CFOs: Four Key Sustainability Data Risks to Watch
Read This
The Business Case for Sustainability Data
Read This
Contact GLYNT.AI

New to GLYNT.AI
© 2025 GLYNT.AI, Inc. | #betterdatafortheplanet | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Compliance Framework


